
MYSPHERA
ID: 4451
29. juli 2022
IoT solution to increase autonomy and quality of life of older adults, supporting and extending independent living in own homes.
ID: 4129
4. maj 2022
NTT Data, part of NTT Group, is a trusted global innovator of IT business services. The company helps clients, as well as society, transform and move confidently into the digital future by offering a portfolio of consulting, application, business process, cloud and infrastructure services. Headquartered in Tokyo in 1988, and operating in more than 50 countries with 139,500 employees, NTT Data has grown to become a top-10 global IT services provider, serving businesses and governments in a variety of industries worldwide.
The health and wellbeing of a community and an individual is an essential matter to NTT Data, and healthcare is therefore a central industry for the company’s efforts to innovate and accelerate digital transformation. By helping healthcare providers, customers and users leverage cutting-edge technology with personalised data, NTT Data seeks to redefine the healthcare industry by making it more human by design and placing the needs of the individual at the center of care.
The solutions offered by NTT Data support healthcare providers in adopting digital touchpoints that integrate processes and relationships between humans and platforms to deliver data-driven, actionable insights for better patient diagnosis, treatment and monitoring. One recent use case unfolds at one of the company’s subsidiaries in the Basque Country where a precision care solution is developed for improved treatment of patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder [1]. These patients are medicated with lithium. The specific treatment and dosage of lithium are individually prescribed based on a variety of humanoid parameters. The precision care solution makes use of IoT, machine learning and artificial intelligence to enable remote monitoring of these parameters and provide objective insights that are essential for clinicians to determine the ideal dose of lithium and treatment for optimal health of each patient.
The incentive of NTT Data to develop an IoT solution for precision care in bipolar disorder treatment derives from a socioeconomic ambition of transitioning healthcare into a more intelligent and resilient ecosystem capable of generating the best health outcomes as well as patient and staff experiences while reducing the cost of care.
“I am working in the health sector because I like that what I do is positive for the society.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
The specific solution developed by NTT Data helps healthcare providers adopt and advance intelligent informatics that extends care beyond the walls of a hospital. Collecting and aggregating data into actionable patient insights supports more advanced and confident clinical decision-making, which defines moments in a patient’s journey and, in turn, paves the way for precision care.
The notion of a precision care solution arose from a request posed by a group of clinicians preoccupied with treating patients that suffered from bipolar disorder. These clinicians expressed concern about the ability of the healthcare system to provide optimal treatment for these patients due to a lack of prerequisites and tools to objectively assess ideal medication dosages. Bipolar disorder is a mental condition, and lithium is a mood stabiliser medication that is applied to ensure balance in the brain. The dose depends on a variety of parameters, such as symptoms, weight, physical activity and sleep quality, and usually ranges from 600 mg to 1200 mg daily, although some patients may require higher doses. Currently, clinicians are responsible for specifying the ideal dose for each individual patient based on the configuration of these parameters. However, these parameters deviate over time, making it difficult for patients to report back and for clinicians to evaluate. Also, studies indicate that reporting of certain parameters, such as activity and sleep patterns, rarely reflect the facts. Essentially, clinicians’ specification of the ‘optimal’ dose often ends up being a subjective and hypothetically biased estimate. Effects of an improper dose of lithium may be fatal: If underdosing, patients are at increased risk of relapse in mood symptoms leading to episodes of depression and/or mania. If overdosing, patients are at risk of hypothyroidism, changes in blood cell counts and reduced kidney function.
NTT Data has developed a precision care solution that addresses this challenge. The solution relies on a prediction tool for healthcare management that is applicable in supporting the treatment of a variety of chronic diseases. Combined with a wristband that collects patient data, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, the solution brings the insights together that make precision medicine possible.
NTT Data started to develop a solution in July 2018 in collaboration with the public healthcare provider in the Basque Country (BIOEF and Osakidetza) and the experienced Research Institute Tecnalia. The partners started to assess relevant parameters and break down the information needed for treatment. From the initial phase of development, IoT capabilities were certain as the foundation for the solution. To this end, the concept of connected wristbands was adopted in order to facilitate the monitoring and collection of relevant patient data.
“The main thing that I have learned in this project was when we started to think about IoT…”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
The solution and its IoT capabilities were tested in a range of clinical studies and workshops with clinicians where the partners would gain feedback and adapt the solution accordingly. NTT Data’s initial idea was to develop the coding necessary to connect to the wristband (in order to collect the data, transmit it directly to a server, aggregate and analyse it, etc.). However, during the first clinical study they learned that the requirements of each wristband differed, and direct connectivity would necessitate individual codes. Therefore, NTT Data decided to take on a collaborative approach to solve the challenge and discarded the idea of developing the entire solution themselves. By partnering up with a carefully selected external wristband provider, NTT Data could now outsource the data collection of the backend solution while adding a supplementary application to the solution that would also allow the patients to engage with their own health information. By integrating servers with the external partner, NTT Data succeeds to ease code development and maintenance while letting users of the solution benefit from regular technological evolutions enforced by the partner.
The final precision care solution is fully developed and tested, and the next step is commercialisation and implementation in healthcare facilities, for clinicians and bipolar disorder diagnosed patients to start using it in real treatment scenarios. This deployment will grow into mature reference cases that shall serve as proof of concept for the further market adoption. For the solution to penetrate international markets, the strategy is to leverage the commercial capacity of NTT Data’s presence all over the world. Although the solution is new to the market and never seen before in the healthcare domain, NTT Data predicts it will be successful due to its potential to accelerate pharmaceutical R&D and help enhance the global level of medical precision care.
The solution offered by NTT Data covers remote monitoring of patient data and a platform that via artificial intelligence calculates and specifies a precise treatment for each individual patient.
The solution relies on data collected by a wristband, which is worn by the patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder. The wristband captures a variety of data sources related to the patient’s sleep patterns (hours, interruptions, quality etc.), activity patterns (steps, sports, calories etc.) and biological factors (heart rate, pulse, etc.). The data is transmitted via Bluetooth to a mobile application hosted by the patient’s mobile phone. When connected to the internet, the mobile phone transmits the data to an external server owned by the manufacturer of the wristband. This server is integrated with a server owned by NTT Data where the patient’s health data is analysed and processed. The data is used as input for machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence models, which enable the platform to calculate the ideal dose of lithium and specify the optimal treatment for the specific patient.
“So all these things are calculated with an artificial intelligence model that estimates the best dosage for a patient.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
The aggregated data can be stored either in the cloud or on-premise (on the server owned by the healthcare facility), depending on the request of the customer. The data can be accessed through an application developed for the clinicians, which presents the information via a user interface at the site of the healthcare facility.
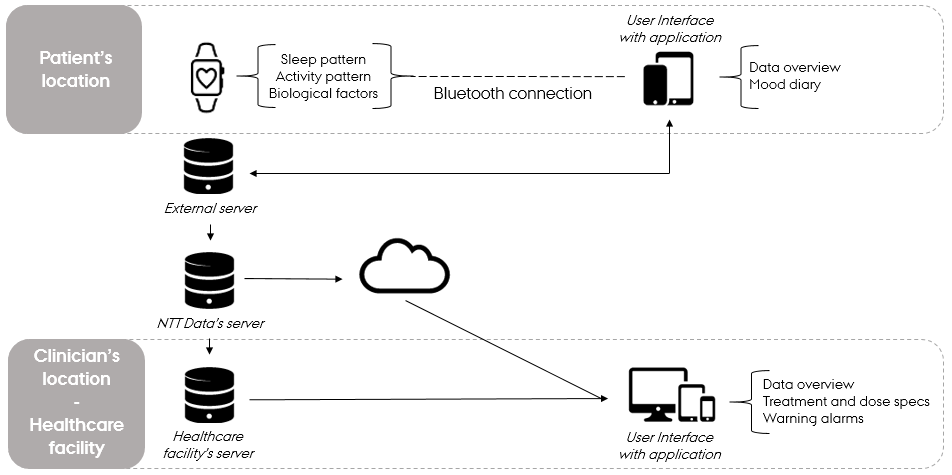
The user interface designed for patients (mobile application), enables them to get a data overview and track the various parameters measured by the wristband. The application allows the user to submit additional information as well, for example in the ‘mood diary’ where patients are encouraged to keep a daily journal on their mental state, providing information on how they are feeling and why they are feeling that way.
The user interface designed for clinicians (web application), enables them to get a digital overview of all relevant information on the health of the patient – both the real-time information collected by the wristband and historical information from the facility’s electronic health records – which is presented in various graphs and accompanied by the person-specific treatment and medication dosage. Another feature of the application is an alarm system that shows warnings to the clinician if there is a reason for concern about the health of the bipolar disorder diagnosed patient. These alarms are triggered by continuous negative journaling in the mood diary, and if the patient has not connected to the application over a longer period of time.
The offering of NTT Data automates the care journey for bipolar disorder treatment and is a great example on how artificial intelligence models and precision care can offer improved preventive, diagnostic and treatment options across a genomic landscape at a resolution and scale unimaginable just a few years ago.
The development of NTT DATA’s solution is tapping directly into the socioeconomic ambition of transitioning healthcare into a more intelligent industry capable of generating better health outcomes. The precision care solution contributes to accelerating innovation and transformation across the digital health ecosystem while helping to sustain value throughout the individual care journey.
The solution presents society with an opportunity to fundamentally transform the way people interact with healthcare. The intelligence and data-driven insights of precision care solutions can help to optimise staff allocation and productivity while improving efficiency and quality of the treatments – in this case for bipolar disorder diagnosed patients. Hence, the direct outcome of the solution is the assurance that an ideal dose of lithium is provided, and thereby that each individual patient receives optimal and improved treatment.

The derived effect of the solution is improved treatment for bipolar diagnosed patients, which gives rise to a variety of valuable outcomes for the users and customers of the solution as well. The users include two different groups: the clinicians that specify treatment for patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder and the patients receiving that treatment, whereas the customers of the solution are public and private healthcare facilities. The specific outcomes for users and customers of the solution are outlined in the following.
Clinicians’ outcomes
Patients’ outcomes
Healthcare facilities’ outcomes
“We are able to avoid admissions due to this solution. For me, that will be the most valuable outcome.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
Considering the outcome of NTT Data’s precision care solution for the entire healthcare industry, it will improve the healthcare workforce’s experience of providing care while lowering healthcare costs, and it will also improve the patient’s experience of care, and, eventually, improve the general health of the population.
Since NTT Data introduced the first clinicians to the idea of precision care and the value to gain from integrating intelligence and personalisation in the treatment of bipolar disorder, many alterations and adaptations have transpired in the process from idea to developed solution. The company has gained many learnings along the way; some with transmissible value for other actors manoeuvring in the IoT ecosystem.
Offering an IoT-based solution to an industry characterised by traditional service practice and strict regulations does, however, imply some adoption resistance and a need for more meticulous development. NTT Data experienced this challenge head on in the early development of the solution as they got acquainted with the European Medical Device Regulation [2].
“We started the project without having that in mind. It was a big challenge for us to adapt to regulations and to conduct clinical studies.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
NTT Data were able to overcome the challenge although it was costly on time and resources, and it has taught the company the significance of comprehensively exploring an industry this traditional before entering it with a disruptive solution.
As of late 2021, NTT Data’s precision care solution is commercially ready for the market. The feedback on development and testing of the solution indicates that optimistic prospects are to be expected for the soon commercialisation and adoption. NTT Data considers a number of points to be vital for the future success of their IoT solution. Taking departure in the development process and its appertaining test results and user feedback, these points are compiled into a list of recommendations below.
1. Establish alliances with experts
NTT Data refers to this as the main processual change in their own predefined plan for the development of the solution.
“Try to work more in alliances with IoT companies.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
The shift in approach from making the wristband themselves to collaborating with wristband manufacturers has turned out as great learning and is considered an essential decision for the current development success.
2. Be flexible in your collaborations
“Try to collaborate with different IoT companies and be able to work with any of them.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
NTT Data points out that if you allow your entire business model to depend on only one collaborative partner, you limit yourself from harvesting extraordinary performance results in several business activities. There are so many actors in the field of IoT, their key performance is often specialised, and spotting both the specialisation and the best performers is a difficult endeavour. Hence, developing a solution that can function and integrate with numerous partners and their solutions offers a far more favourable position.
3. Offer enviable solutions – and use this as a lever for commercialisation
“Some products are sold with the argument that ‘I want it too!’ So we expect that once we are able to implement it by the first customers, we will be able to spread it.”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
Solutions of the same calibre as NTT Data’s precision care, i.e. with the potential to transform the practices of an entire industry, need solid clinical foundation and commercial arguments before pursuing market scalability. Commercial success hinges on the initial implementations (in healthcare facilities), where the potential users must experience and reckon the value of using the solution, for them to pull derived demand.
One final reflection from NTT Data calls attention to the fear of failure that many IoT innovators may have throughout the development process. This fear can be conjured away by rapid testing and listening to users which can then reveal the true prospects of success for one’s solution.
“Of course we always have a fear… But then we have feedback!”
Arkaitz Cámara Etxebarria, Health Project Manager at NTT Data
[1] Bipolar disorder: A mental disorder that causes unusual shifts in mood, energy, activity levels, concentration and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks. The disorder includes emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). Also known as manic depression.
[2] The European Medical Device Regulation (MDR): New set of regulations that governs the production and distribution of medical devices in Europe, and compliance with the regulation is mandatory for medical device companies that want to sell their products in the European marketplace.
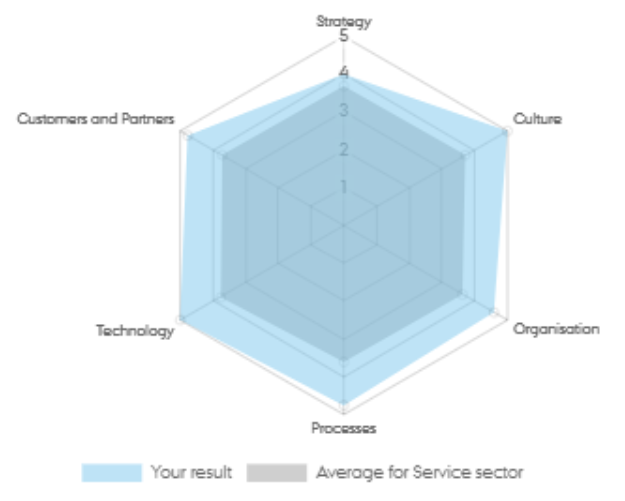
NTT Data assumes a high level of digital maturity with an overall score of 4.68. The score indicates that the digital capabilities of the company are vastly mature, and that they perform above average for the service sector.
The Digital Maturity Assessment Tool is copyrighted by Associate Professor and PhD Annabeth Aagaard, Director at the Interdisciplinary Centre for Digital Business Development, Aarhus University. To get the digital maturity of your company mapped out, click here.

Copyright notice: © 2020 – 2023 EU-IoT Consortium.
This material was produced as part of the EU-IoT project, grant ID 956671, and is funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Programme under topic ID ICT-56-2020.
EU-IoT is the European IoT Hub. The EU-IoT project works towards growing a sustainable and comprehensive ecosystem for Next Generation Internet of Things.
Source of origin: Information to document this use case originates from a network collaboration w. IoT Next Club (IoT community associated with the NGIoT initiative); Case period: 2021-2022.
